MegaplanIT helps organizations select the appropriate CMMC certification level (1 through 5), identify gaps between their current state and the requirements needed to achieve that level, and develop an internal project plan to remediate those gaps and prepare for a successful audit once the certification requirements are finalized and assessors are authorized.
Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC)
The CMMC is a new government standard that combines various cybersecurity standards and best practices into a grading scale of maturity against which the assessed organization is compared.
What is CMMC?
The DoD’s Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC) will serve as the verification mechanism to ensure appropriate levels of cybersecurity practices and processes are in place across the DoD’s industry partners and suppliers. The CMMC combines various cybersecurity standards and best practices, listed below:
FAR Clause 52.204-21
NIST SP 800-171 Rev 1
Draft NIST SP 800-171B
CIS Controls v7.1
NIST Framework for Improving Critical Infrastructure Cybersecurity (CSF) v1.1
CERT Resilience Management Model (CERT RMM) v1.2
NIST SP 800-53 Rev 4
Others such as, UK NCSC Cyber Essentials, or AU ACSC Essential Eight

WHY IS THE CMMC USEFUL?
All new contracts and Requests for Information from the Department of Defense (DoD) and its vendors will require specific levels of CMMC compliance by 4Q 2020. Any company wishing to do business with the DoD, or a DoD vendor will need to prove their compliance with CMMC. In addition, the CMMC provides a gauge for the auditing of organizational processes and procedures along with appropriate supporting evidence to expose areas in need of improvement to protect intellectual property and sensitive information. The Council of Economic Advisors estimates the cost of malicious cyber activity in the billions of dollars for the U.S. economy alone. Strong cybersecurity controls are one step all organizations can take to protect their most valuable assets, regardless of the industry they serve. Certification levels for each organization are validated by a CMMC Third Party Assessment Organization authorized and trained to perform the work by the CMMC Accreditation Body. Organization’s compliance with CMMC will go beyond the current DFARS 252.204-7012 self-attestation and is valid for three years.
CMMC Compliance and Cybersecurity Best Practices
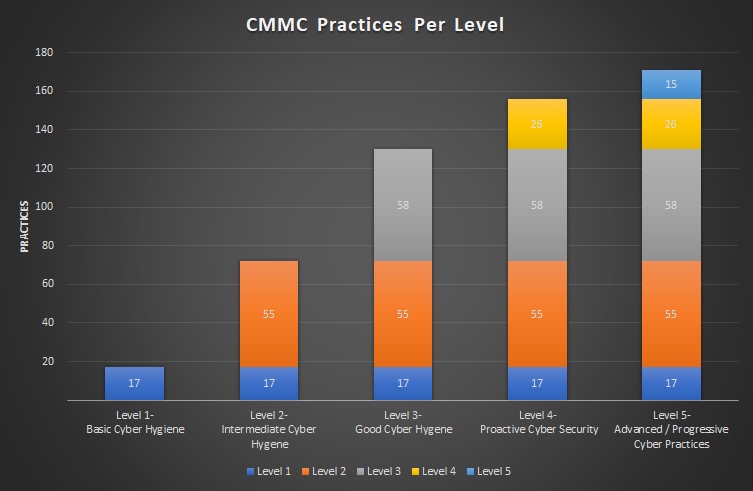
The CMMC model contains 171 cybersecurity best practices.
Level 1
Basic safeguarding of client data
Level 2
Intermediate implemented safeguards in place
Level 3
Good broad protection of Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI)
Level 4
Proactive Reduction of Risk from Advanced Persistent Threats
Level 5
Advanced Reduction of Persistent Threats/Progressive Security
Additional information on CMMC model may be found here.
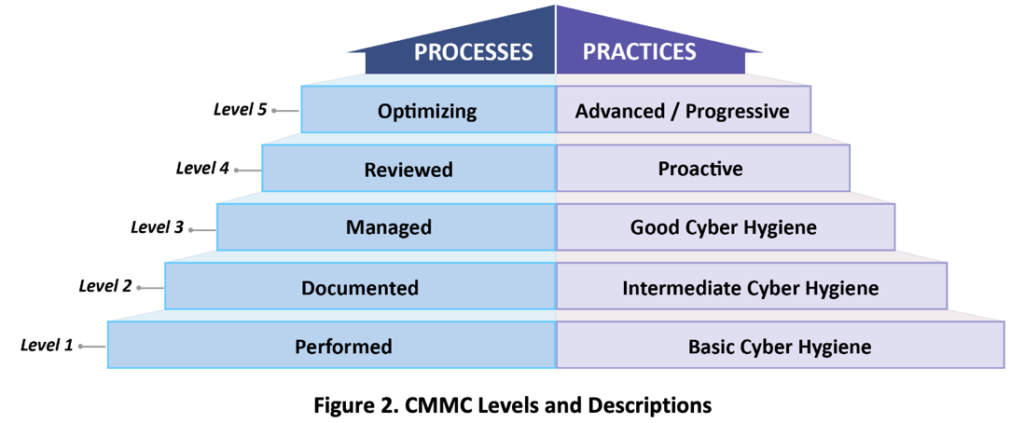
Levels & Descriptions
Each domain contains a set of defined processes and practices which align to the level of practice progression, or implementation, as defined above and in the right side of the graphic shown here. In addition, the institutionalization, or maturity, of the processes and practices is assessed as shown in the left side of the graphic. An organization must demonstrate both maturity and implementation of processes and practices to be certified at a given level.
Key Benefits
How CMMC Audits Strengthen Your Security and Compliance
CMMC works much like a NIST standard wherein 17 domains of controls and procedures are audited against an established standard. These areas include:
- Access Control (AC)
- Awareness and Training (AT)
- Asset Management (AM)
- Audit Accountability (AU)
- Configuration Management (CM)
- Identification and Authentication (IA)
- Incident Response (IR)
- Maintenance (MA)
- Personnel Security (PS)
- Recovery (RE)
- Risk Management (RM)
- Security Assessment (CA)
- Situational Awareness (SA)
- System and Communication Protection (SC)
- System and Information Integrity (SI)

HOW IT WORKS
The CMMC Readiness Process
Currently, the CMMC Accreditation Body is in the process of developing the standard to be used for applying the model and preparing to certify trainers for educating assessors. Until the CMMC AB has released the training and assessors have been authorized, organizations cannot be audited for CMMC compliance. Instead, organizations should focus on DFARS/NIST SP 800-171 compliance as the minimum preparation for CMMC.
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Step 4
Step 6
Step 1
Project Scope
Our Security specialist will schedule a series of calls to determine the in-scope environment and gather the necessary personnel and resources.
Step 2
Validation of HIPAA security controls
MegaplanIT will test all systems and their respective controls against the HIPAA security compliance standards
Step 3
Draft reports and QA Process
We will draft a report highlighting any significant deficiencies or gaps uncovered during the testing phase.
Step 4
Final HIPAA Report on Compliance
Post-assessment, our security team will provide you with a State of Readiness Report detailing identified risks and vulnerabilities, along with recommended measures for correcting any issues that violate HIPAA.
Step 6
Ongoing security awareness
Your “human element” represents a major vulnerability in terms of information security, MegaplanIT has developed a customized, hassle-free security awareness training portal.
Make Our Team, Your Team!
Our innovative IT security and compliance solutions are designed to deliver customized, cost-effective service on time—because your priorities are our priorities. With a highly qualified team of PCI DSS QSAs, Penetration Testers, and Information Security Consultants here at MegaplanIT, we will assess your unique company and business environment and design a path to security that will fit all of your needs.




























